Melt blowing
What is meltblown nonwoven?

The melt-blown nonwoven fabric is known as the "heart of the mask", disperses molten plastic through high-speed hot air, and spins the polymer melt through the spinneret of the ultra-fine nozzle, making it a high-performance polypropylene melt-blown filter material. Fibers are extremely thinner than other materials.
Introduction
Melt blowing is a conventional fabrication method of micro- and nanofibers where a polymer melt is extruded through small nozzles surrounded by high speed blowing gas.
The randomly deposited fibers form a nonwoven sheet product applicable for filtration, sorbents, apparels and drug delivery systems.
The substantial benefits of melt blowing are simplicity, high specific productivity and solvent-free operation.
It has ultra-fine fibers with shielding, filtering, oil absorption and thermal insulation properties. It has a wide range of fiber fineness and fiber diameters of up to 2µm to 5µm. These ultra-fine fibers can increase the number and surface area of fibers per unit area and can be used as mask materials, air, liquid filter materials, thermal insulation materials, insulation materials, sound insulation materials, environmentally friendly oil-absorbing materials and wipe cloth and other fields.
Melt blowing technology
Melt blowing is a process for manufacture of nonwoven fabric in which thermoplastic polymer is extruded from a die tip having a row of spinneret orifices with typically 25-35 holes/inch. The fibers exiting from the die tip are contacted with converging sheets or jets of hot air to stretch or draw the fibers down to a ultra-fine diameters typically ranging between 2-4 μm . The fibers are then deposited onto a collector in a random manner and to form a nonwoven fabric. The fibers in the web are usually self-entangled enough that additional bonding is not required. The melt blowing process consists of the following elements: extruder, metering pumps, die assembly, compressor or blower, air furnace and air delivery system to die.
Melt-blown web forming
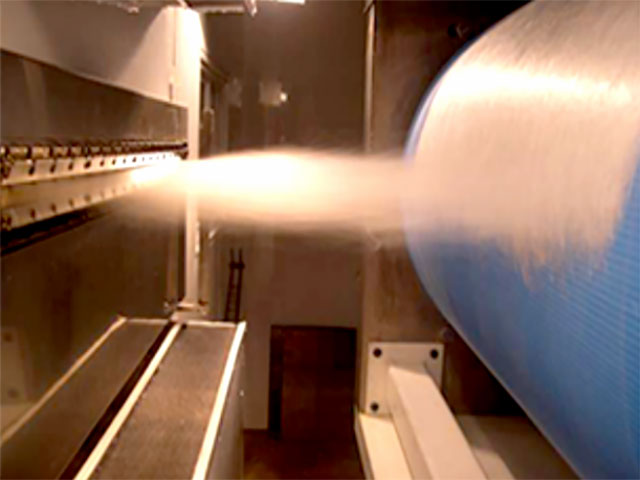

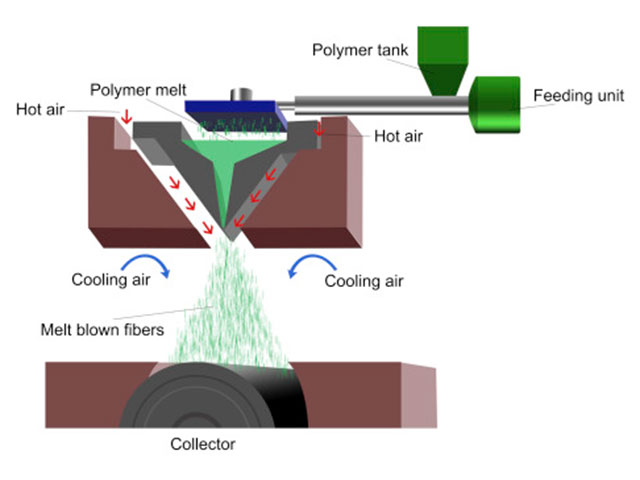
It is a single-step process that transforms polymer as a raw material into the web structure. The basic illustration of the melt-blown process is presented in the pictures above.
Firstly, polymer is melted in an extruder, and then it passes through the die holes in the spinneret and goes into the high-velocity hot airstream. Web structure is established when fibre entanglement occurs.
At the end, blown ultrafine fibres are collected on a rotating drum or a forming belt with a vacuum underneath to generate a nonwoven web.
Polymer properties, air velocity, equipment variables and the degree of fibre entanglement significantly influence the characteristics of the final web structure. In general, in this system fibres with diameter of 1–10 μm can be produced, and any thermoplastic polymer, including biodegradable ones, can be processed.
Polymers
Polymers with thermoplastic behavior are applicable for melt blowing. The main polymer types commonly processed with melt blowing:
- Polypropylene
- Polystyrene
- Polyesters
- Polyurethane
- Polyamides (nylons)
- Polyethylene
- Polycarbonate
Applications of Melt-blown fabrics

The meltblown fabric has a very high density web of fine fibers and it is suitable for applications requiring filtration (particulates, bacteria, fluids). Melt-blown fabrics have generally the same applications as other nonwoven products. The main uses of melt-blown nonwovens and other innovative approaches are as follows.
- Filtration. The porous nonwoven melt-blown fabrics can be used in the filtration of gaseous as well as liquid materials. These applications include water treatment, mask filtering, air purifier, air conditioning filter, filtration of fume and second-hand smoke, car air filtration, fabrication room filtration, etc.
- Sorbents. Nonwovens are capable to retain liquids several times of their own weight. For instance, polypropylene nonwovens are ideal to recollect oil contaminations, river pollution prevention, environmental protection oil absorption, wipe cloth, etc.
- Hygiene products. The high sorption efficiency of melt-blown nonwovens can be exploited in disposable diapers, sanitary napkins and other feminine hygiene products as well.
- Apparels. The good thermal insulation properties, the barrier behavior against fluids combined with breathability make melt-blown nonwovens a great choice for apparels even in harsh environments. Ski equipment, gloves: cold protection padding.
- Drug delivery. Melt blowing is also capable to produce drug-loaded fibers for controlled drug delivery. The high throughput rate (extrusion feeding), solvent-free operation accompanied with the increased surface area of the product make melt blowing a promising new formulation technique.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia